|
Category: natural substances and extractives
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
Physical Properties:
| Assay: | 95.00 to 100.00 %
|
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Soluble in: |
| | water, 0.0333 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) |
Organoleptic Properties:
| |
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). |
| |
| |
Cosmetic Information:
Suppliers:
Safety Information:
| Preferred SDS: View |
| |
| Hazards identification |
| |
| Classification of the substance or mixture |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) |
| None found. |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements |
| |
| Pictogram | |
| |
| Hazard statement(s) |
| None found. |
| Precautionary statement(s) |
| None found. |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
| Dermal Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
| Inhalation Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | natural substances and extractives |
| Recommendation for ginsenoside F2 usage levels up to: | | | not for fragrance use.
|
| |
| Recommendation for ginsenoside F2 flavor usage levels up to: |
| | not for flavor use.
|
Safety References:
References:
Other Information:
Potential Blenders and core components notePotential Uses:
Occurrence (nature, food, other): noteSynonyms:
| (3beta,12beta)-20-(beta-D- | glucopyranosyloxy)-12-hydroxydammar | | 3beta,20-bis(beta-D- | glucopyranosyloxy)dammar-24-en-12beta-ol |
Articles:
| PubMed: | Ginseng polysaccharides enhanced ginsenoside Rb1 and microbial metabolites exposure through enhancing intestinal absorption and affecting gut microbial metabolism. |
| PubMed: | Ciceribacter azotifigens sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from activated sludge. |
| PubMed: | Comparative study on chemical components and anti-inflammatory effects of Panax notoginseng flower extracted by water and methanol. |
| PubMed: | Chryseobacterium ginsengiterrae sp. nov., with Beta-Glucosidase Activity Isolated from Soil of a Ginseng Field. |
| PubMed: | Daejeonia ginsenosidivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a ginsenoside-transforming bacterium isolated from lake water. |
| PubMed: | Ginsenoside F2 induces the release of mediators associated with Anaphylactoid reactions. |
| PubMed: | Production of the Rare Ginsenoside Rh2-MIX (20(S)-Rh2, 20(R)-Rh2, Rk2, and Rh3) by Enzymatic Conversion Combined with Acid Treatment and Evaluation of Its Anti-Cancer Activity. |
| PubMed: | Fermentation of protopanaxadiol type ginsenosides (PD) with probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus. |
| PubMed: | iTRAQ-Based Proteomic Analysis of Ginsenoside F2on Human Gastric Carcinoma Cells SGC7901. |
| PubMed: | Cloning and Characterization of Ginsenoside-Hydrolyzing β-Glucosidase fromLactobacillus brevisThat Transforms Ginsenosides Rb1 and F2 into Ginsenoside Rd and Compound K. |
| PubMed: | Ginsenosides, ingredients of the root of Panax ginseng, are not substrates but inhibitors of sodium-glucose transporter 1. |
| PubMed: | Protective effects of ginsenoside F2 on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced skin inflammation in mice. |
| PubMed: | Sphingobacterium jejuense sp. nov., with ginsenoside-converting activity, isolated from compost. |
| PubMed: | Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside C-K by endophytic fungus Arthrinium sp. GE 17-18 isolated from Panax ginseng. |
| PubMed: | Pseudobacter ginsenosidimutans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from ginseng cultivating soil. |
| PubMed: | The chemoattractant potential of ginsenosides in the ginseng - Pythium irregulare pathosystem. |
| PubMed: | Production of Ginsenoside F2 by Using Lactococcus lactis with Enhanced Expression of β-Glucosidase Gene from Paenibacillus mucilaginosus. |
| PubMed: | Ninjin'yoeito and ginseng extract prevent oxaliplatin-induced neurodegeneration in PC12 cells. |
| PubMed: | Effects of broad-spectrum antibiotics on the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside Rb1: a study on rats׳ gut microflora influenced by lincomycin. |
| PubMed: | The Bioconversion of Red Ginseng Ethanol Extract into Compound K by Saccharomyces cerevisiae HJ-014. |
| PubMed: | Characterization of recombinant β-glucosidase from Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus and biotransformation of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb 2, Rc, and Rd. |
| PubMed: | Ginsenoside F2 reduces hair loss by controlling apoptosis through the sterol regulatory element-binding protein cleavage activating protein and transforming growth factor-β pathways in a dihydrotestosterone-induced mouse model. |
| PubMed: | Ginsenoside F2 possesses anti-obesity activity via binding with PPARγ and inhibiting adipocyte differentiation in the 3T3-L1 cell line. |
| PubMed: | The inductive effect of ginsenoside F2 on hair growth by altering the WNT signal pathway in telogen mouse skin. |
| PubMed: | Highly selective hydrolysis for the outer glucose at the C-20 position in ginsenosides by β-glucosidase from Thermus thermophilus and its application to the production of ginsenoside F2 from gypenoside XVII. |
| PubMed: | [Chemical constituents from processed rhizomes of Panax notoginseng]. |
| PubMed: | Characterization of a ginsenoside-transforming β-glucosidase from Paenibacillus mucilaginosus and its application for enhanced production of minor ginsenoside F₂. |
| PubMed: | Enzyme-modified Panax ginseng inhibits UVB-induced skin aging through the regulation of procollagen type I and MMP-1 expression. |
| PubMed: | Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 via the gypenoside pathway by human gut bacteria. |
| PubMed: | Ginsenoside F(2) induces apoptosis in humor gastric carcinoma cells through reactive oxygen species-mitochondria pathway and modulation of ASK-1/JNK signaling cascade in vitro and in vivo. |
| PubMed: | Biotransformation of saponins by endophytes isolated from Panax notoginseng. |
| PubMed: | Enzymatic Biotransformation of Ginsenoside Rb1 and Gypenoside XVII into Ginsenosides Rd and F2 by Recombinant β-glucosidase from Flavobacterium johnsoniae. |
| PubMed: | [Screening of pregnane X receptor activation from ginsenosides]. |
| PubMed: | Biotransformation and metabolic profile of American ginseng saponins with human intestinal microflora by liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. |
| PubMed: | Microbial transformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to compound K by Lactobacillus paralimentarius. |
| PubMed: | Lactobacillus ginsenosidimutans sp. nov., isolated from kimchi with the ability to transform ginsenosides. |
| PubMed: | Purification and characterization of a ginsenoside Rb(1)-hydrolyzing β-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger KCCM 11239. |
| PubMed: | Ginsenosidases and the pathogenicity of Pythium irregulare. |
| PubMed: | Ginsenoside F2 induces apoptosis accompanied by protective autophagy in breast cancer stem cells. |
| PubMed: | Anti-Cancer Effect of Ginsenoside F2 against Glioblastoma Multiforme in Xenograft Model in SD Rats. |
| PubMed: | Biotransformation of Ginsenoside Rb1 to Prosapogenins, Gypenoside XVII, Ginsenoside Rd, Ginsenoside F2, and Compound K by Leuconostoc mesenteroides DC102. |
| PubMed: | Phycicoccus ginsenosidimutans sp. nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field. |
| PubMed: | Partial purification and characterization of three ginsenoside-metabolizing beta-glucosidases from Pythium irregulare. |
| PubMed: | Comparative analysis on microbial and rat metabolism of ginsenoside Rb1 by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. |
| PubMed: | Development and validation of a reversed-phase HPLC method for quantitative determination of ginsenosides Rb1, Rd, F2, and compound K during the process of biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1. |
| PubMed: | Microbial conversion of ginsenoside Rb1 to minor ginsenoside F2 and gypenoside XVII by Intrasporangium sp. GS603 isolated from soil. |
| PubMed: | Marked production of ginsenosides Rd, F2, Rg3, and compound K by enzymatic method. |
| PubMed: | Conversion of major ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside F2 by Caulobacter leidyia. |
| PubMed: | In vitro metabolism of ginsenosides by the ginseng root pathogen Pythium irregulare. |
| PubMed: | [Metabolism of ginsenoside Rb1 and panaxadiol saponins by fungi]. |
| PubMed: | [Minor saponins from leaves of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer]. |
| PubMed: | Studies on absorption, distribution, excretion and metabolism of ginseng saponins. VII. Comparison of the decomposition modes of ginsenoside-Rb1 and -Rb2 in the digestive tract of rats. |
| PubMed: | Studies on absorption, distribution, excretion and metabolism of ginseng saponins. V. The decomposition products of ginsenoside Rb2 in the large intestine of rats. |
|
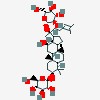 3D/inchi
3D/inchi
