Articles:
campestan-2alpha,3alpha,22R,23R-tetrol
Notes:
None found
| CAS Number: | 87833-54-3 | 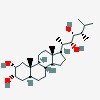 3D/inchi 3D/inchi
|
| Nikkaji Web: | J146.605D | |
| XlogP3: | 6.30 (est) | |
| Molecular Weight: | 450.70330000 | |
| Formula: | C28 H50 O4 | |
| NMR Predictor: | Predict (works with chrome or firefox) | |
Category: natural substances and extractives
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
| Google Scholar: | Search |
| Google Books: | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "volatile" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "flavor" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "odor" | Search |
| Google Patents: | Search |
| US Patents: | Search |
| EU Patents: | Search |
| Pubchem Patents: | Search |
| PubMed: | Search |
| NCBI: | Search |
Physical Properties:
| Assay: | 95.00 to 100.00 % |
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Soluble in: | |
| water, 0.07423 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) | |
Organoleptic Properties:
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). | |
Cosmetic Information:
| None found |
Suppliers:
| None found |
Safety Information:
| Hazards identification | |
| Classification of the substance or mixture | |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) | |
| None found. | |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements | |
| Pictogram | |
| Hazard statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
| Dermal Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
| Inhalation Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | natural substances and extractives | ||
| Recommendation for 6-deoxocastasterone usage levels up to: | |||
| not for fragrance use. | |||
| Recommendation for 6-deoxocastasterone flavor usage levels up to: | |||
| not for flavor use. | |||
Safety References:
| EPI System: | View |
| AIDS Citations: | Search |
| Cancer Citations: | Search |
| Toxicology Citations: | Search |
| EPA ACToR: | Toxicology Data |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (SRS): | Registry |
| Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary : | 13870433 |
| National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: | Data |
| (2R,3S,5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,17R)-17-[(2S,3R,4R,5S)-3,4-dihydroxy-5,6-dimethylheptan-2-yl]-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-2,3-diol |
References:
| (2R,3S,5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,17R)-17-[(2S,3R,4R,5S)-3,4-dihydroxy-5,6-dimethylheptan-2-yl]-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-2,3-diol | |
| NIST Chemistry WebBook: | Search Inchi |
| Pubchem (cid): | 13870433 |
| Pubchem (cas): | 87833-54-3 |
Other Information:
| (IUPAC): | Atomic Weights of the Elements 2011 (pdf) |
| Videos: | The Periodic Table of Videos |
| tgsc: | Atomic Weights use for this web site |
| (IUPAC): | Periodic Table of the Elements |
| CHEBI: | View |
| KEGG (GenomeNet): | C15802 |
| HMDB (The Human Metabolome Database): | HMDB33984 |
| FooDB: | FDB012216 |
| VCF-Online: | VCF Volatile Compounds in Food |
| ChemSpider: | View |
Potential Blenders and core components note
| None Found | ||
Potential Uses:
| None Found |
Occurrence (nature, food, other): note
| camellia sinensis Search Trop Picture | |
| cupressus arizonica pollen Search Trop Picture | |
| phaseolus vulgaris Search Trop Picture | |
| terminalia chebula Search Trop Picture |
Synonyms:
| campestan-2alpha,3alpha,22R,23R-tetrol | |
| (2R,3S,5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S,17R)-17-[(2S,3R,4R,5S)-3,4- | dihydroxy-5,6-dimethylheptan-2-yl]-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-2,3-diol |