|
Category: cosmetic ingredient for skin conditioning
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
Physical Properties:
| Assay: | 95.00 to 100.00 %
|
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Soluble in: |
| | water, 1.393e+005 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) |
Organoleptic Properties:
| |
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). |
| |
| |
Cosmetic Information:
Suppliers:
Safety Information:
| Preferred SDS: View |
| |
| Hazards identification |
| |
| Classification of the substance or mixture |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) |
| None found. |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements |
| |
| Pictogram | |
| |
| Hazard statement(s) |
| None found. |
| Precautionary statement(s) |
| None found. |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
| Dermal Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
| Inhalation Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | cosmetic ingredient for skin conditioning |
| Recommendation for fulvic acid usage levels up to: | | | not for fragrance use.
|
| |
| Recommendation for fulvic acid flavor usage levels up to: |
| | not for flavor use.
|
Safety References:
| EPI System: | View |
| Cancer Citations: | Search |
| Toxicology Citations: | Search |
| EPA ACToR: | Toxicology Data |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (SRS): | Registry |
| Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary : | 5359407 |
| National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: | Data |
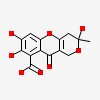
| | 3,7,8-trihydroxy-3-methyl-10-oxo-1,4-dihydropyrano[4,3-b]chromene-9-carboxylic acid |
| Chemidplus: | 0000479663 |
References:
| | 3,7,8-trihydroxy-3-methyl-10-oxo-1,4-dihydropyrano[4,3-b]chromene-9-carboxylic acid |
| NIST Chemistry WebBook: | Search Inchi |
| Pubchem (cid): | 5359407 |
| Pubchem (sid): | 134974174 |
Other Information:
Potential Blenders and core components notePotential Uses:
Occurrence (nature, food, other): noteSynonyms:
| 3,4- | dihydro-3,7,8-trihydroxy-3-methyl-10-oxo-1H,10H-pyrano(4,3-b)(1)benzopyran-9-carboxylic acid | | 1H,3H- | pyrano[4,3-b][1]benzopyran-9-carboxylic acid, 4,10-dihydro-3,7,8-trihydroxy-3-methyl-10-oxo | | 3,7,8- | trihydroxy-3-methyl-10-oxo-1,4-dihydropyrano[4,3-b]chromene-9-carboxylic acid |
Articles:
| PubMed: | Distribution and translocation of selenium from soil to highland barley in the Tibetan Plateau Kashin-Beck disease area. |
| PubMed: | [Vermicomposting of different organic materials and three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopic characterization of their dissolved organic matter]. |
| PubMed: | Characterizing the interaction between uranyl ion and fulvic acid using regional integration analysis (RIA) and fluorescence quenching. |
| PubMed: | [Spectrum characteristics of leaching components from co-contaminated loess in ex-situ column washing reaction]. |
| PubMed: | Fulvic acid mediates chromium (Cr) tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) through lowering of Cr uptake and improved antioxidant defense system. |
| PubMed: | Isolation and characterization of Chinese standard fulvic acid sub-fractions separated from forest soil by stepwise elution with pyrophosphate buffer. |
| PubMed: | The use of solid-phase fluorescence spectroscopy in the characterisation of organic matter transformations. |
| PubMed: | Evaluation of monitoring indicators for the post-closure care of a landfill for MSW characterized with low lignin content. |
| PubMed: | Evaluation of humic substances during co-composting of food waste, sawdust and Chinese medicinal herbal residues. |
| PubMed: | Relationship between anaerobic digestion of biodegradable solid waste and spectral characteristics of the derived liquid digestate. |
| PubMed: | Effect of presence of cellulose in the freshwater sediment on the performance of sediment microbial fuel cell. |
| PubMed: | Soil metabolism of [14C]methiozolin under aerobic and anaerobic flooded conditions. |
| PubMed: | Characterization of the atrazine sorption process on Andisol and Ultisol volcanic ash-derived soils: kinetic parameters and the contribution of humic fractions. |
| PubMed: | Can nutraceuticals prevent Alzheimer's disease? Potential therapeutic role of a formulation containing shilajit and complex B vitamins. |
| PubMed: | Photodegradation of ormetoprim in aquaculture and stream-derived dissolved organic matter. |
| PubMed: | Effects of soil properties on the transfer of cadmium from soil to wheat in the Yangtze River delta region, China--a typical industry-agriculture transition area. |
| PubMed: | Investigation into organic phosphorus species in sediments of Baiyangdian Lake in China measured by fractionation and ³¹P NMR. |
| PubMed: | Abiotic reduction of pendimethalin and trifluralin in controlled and natural systems containing Fe(II) and dissolved organic matter. |
| PubMed: | Novel software for data analysis of Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectra applied to natural organic matter. |
| PubMed: | Complementary multianalytical approach to study the distinctive structural features of the main humic fractions in solution: gray humic acid, brown humic acid, and fulvic acid. |
| PubMed: | Influence of fulvic acids and copper ions on thiram determination in water. |
| PubMed: | Characterization of brewery wastewater with spectrofluorometry analysis. |
| PubMed: | Multivariate statistical analysis of mass spectra as a tool for the classification of the main humic substances according to their structural and conformational features. |
| PubMed: | Maturity assessment of composted olive mill wastes using UV spectra and humification parameters. |
| PubMed: | Bioconversion of wastes from the olive oil and confectionary industries: spectroscopic study of humic acids. |
| PubMed: | Environmental photochemistry of tylosin: efficient, reversible photoisomerization to a less-active isomer, followed by photolysis. |
| PubMed: | Characterization of humic substances derived from swine manure-based compost and correlation of their characteristics with reactivities with heavy metals. |
| PubMed: | Changes in organic matter and residual effect of amendment with two-phase olive-mill waste on degraded agricultural soils. |
| PubMed: | Evolution of the fulvic acid fractions during co-composting of olive oil mill wastewater sludge and tree cuttings. |
| PubMed: | Water remediation by micelle-clay system: case study for tetracycline and sulfonamide antibiotics. |
| PubMed: | Modification of soil humic matter after 4 years of compost application. |
| PubMed: | Compost effect on soil humic acid: A NMR study. |
| PubMed: | Humic substances can modulate the allelopathic potential of caffeic, ferulic, and salicylic acids for seedlings of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) and tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). |
| PubMed: | Influence of water chemistry on the acute toxicity of copper and zinc to the cladoceran Ceriodaphnia cf dubia. |
| PubMed: | Long-time fulvic acid supplementation modulates hydroxylysyl glycosylation of collagen in mice. |
| PubMed: | Towards sustainable use of potassium in pineapple waste. |
| PubMed: | Analysis of carbon and nitrogen forms in soil fractions after the addition of 15N-compost by 13C and 15N nuclear magnetic resonance. |
| PubMed: | Influence of organic matter on the uptake of cadmium, zinc, copper and iron by sorghum plants. |
| PubMed: | Characterization and biological activities of humic substances from mumie. |
| PubMed: | Aerobic soil metabolism of a new herbicide, LGC-42153. |
| PubMed: | Retention and extractability of phenol, cresol, and dichlorophenol exposed to two surface soils in the presence of horseradish peroxidase enzyme. |
| PubMed: | Studies on bound (14)C-chlorsulfuron residues in soil. |
| PubMed: | Aquatic humic substances inhibit clastogenic events in germinating seeds of herbaceous plants. |
| PubMed: | Microbial release and degradation of nonextractable anilazine residues. |
| PubMed: | Intestinal absorption of copper from drinking water containing fulvic acids and an infant formula mixture studied in a suckling rat model. |
| PubMed: | Fulvic and humic acids decrease the absorption of cadmium in the rat intestine. |
| PubMed: | Study on the pathogenic factors of Kashin-Beck disease. |
|
 3D/inchi
3D/inchi

