Articles:
kaempferol-3-O-gal-rham-7-O-rhamnoside
Notes:
None found
| CAS Number: | 301-19-9 | 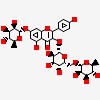 3D/inchi 3D/inchi
|
| ECHA EINECS - REACH Pre-Reg: | 206-113-3 | |
| FDA UNII: | 75RT1VGM60 | |
| Nikkaji Web: | J11.402B | |
| MDL: | MFCD00016940 | |
| XlogP3-AA: | -2.20 (est) | |
| Molecular Weight: | 740.66660000 | |
| Formula: | C33 H40 O19 | |
| NMR Predictor: | Predict (works with chrome or firefox) | |
Category: natural substances and extractives
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
| Google Scholar: | Search |
| Google Books: | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "volatile" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "flavor" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "odor" | Search |
| Google Patents: | Search |
| US Patents: | Search |
| EU Patents: | Search |
| Pubchem Patents: | Search |
| PubMed: | Search |
| NCBI: | Search |
Physical Properties:
| Assay: | 95.00 to 100.00 % |
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Melting Point: | 250.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg |
| Boiling Point: | 1064.40 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg (est) |
| Flash Point: | 636.00 °F. TCC ( 335.70 °C. ) (est) |
| logP (o/w): | 0.890 (est) |
| Soluble in: | |
| water, 1.295e+004 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) | |
Organoleptic Properties:
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). | |
Cosmetic Information:
| None found |
Suppliers:
| Alfa Biotechnology |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Robinin 98% |
| BOC Sciences |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Robinin |
| Carbosynth |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Robinin |
| ExtraSynthese |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Robinin (HPLC) ≥90% |
| Sigma-Aldrich: Sigma |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Robinin ≥90.0% (HPLC) |
Safety Information:
| Preferred SDS: View | |
| Hazards identification | |
| Classification of the substance or mixture | |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) | |
| None found. | |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements | |
| Pictogram | |
| Hazard statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
| Dermal Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
| Inhalation Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | natural substances and extractives | ||
| Recommendation for robinin usage levels up to: | |||
| not for fragrance use. | |||
| Recommendation for robinin flavor usage levels up to: | |||
| not for flavor use. | |||
Safety References:
| EPI System: | View |
| AIDS Citations: | Search |
| Cancer Citations: | Search |
| Toxicology Citations: | Search |
| EPA ACToR: | Toxicology Data |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (SRS): | Registry |
| Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary : | 5281693 |
| National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: | Data |
| WGK Germany: | 3 |
| Chemidplus: | 0000301199 |
References:
| NIST Chemistry WebBook: | Search Inchi |
| Pubchem (cid): | 5281693 |
| Pubchem (sid): | 135048049 |
Other Information:
| (IUPAC): | Atomic Weights of the Elements 2011 (pdf) |
| Videos: | The Periodic Table of Videos |
| tgsc: | Atomic Weights use for this web site |
| (IUPAC): | Periodic Table of the Elements |
| CHEBI: | View |
| KEGG (GenomeNet): | C10178 |
| HMDB (The Human Metabolome Database): | Search |
| FooDB: | FDB002528 |
| VCF-Online: | VCF Volatile Compounds in Food |
| ChemSpider: | View |
| Wikipedia: | View |
Potential Blenders and core components note
| None Found | ||
Potential Uses:
| None Found |
Occurrence (nature, food, other): note
| bean adzuki bean leaf Search Trop Picture | |
| bean mung bean plant Search Trop Picture | |
| bean mung bean sprout Search Trop Picture | |
| lotus indian lotus plant Search Trop Picture |
Synonyms:
| kaempferol-3-O-gal-rham-7-O-rhamnoside |
