Articles:
flavone, 5,7-dihydroxy-4',6-dimethoxy- (8CI)
Notes:
from cirsium japonicum d. c..
| CAS Number: | 520-12-7 | 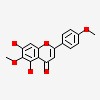 3D/inchi 3D/inchi
|
| ECHA EINECS - REACH Pre-Reg: | 208-286-0 | |
| FDA UNII: | 4U3UZ1K35N | |
| Nikkaji Web: | J6.599D | |
| XlogP3: | 2.00 (est) | |
| Molecular Weight: | 314.29378000 | |
| Formula: | C17 H14 O6 | |
| BioActivity Summary: | listing | |
| NMR Predictor: | Predict (works with chrome or firefox) | |
Category: natural substances and extractives
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
| Google Scholar: | Search |
| Google Books: | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "volatile" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "flavor" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "odor" | Search |
| Google Patents: | Search |
| US Patents: | Search |
| EU Patents: | Search |
| Pubchem Patents: | Search |
| PubMed: | Search |
| NCBI: | Search |
Physical Properties:
| Assay: | 95.00 to 100.00 % |
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Melting Point: | 221.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg |
| Boiling Point: | 565.50 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg (est) |
| Flash Point: | 414.00 °F. TCC ( 212.30 °C. ) (est) |
| logP (o/w): | 2.640 (est) |
| Soluble in: | |
| water, 17.64 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) | |
Organoleptic Properties:
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). | |
Cosmetic Information:
| None found |
Suppliers:
| BOC Sciences |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Pectolinarigenin |
| Coompo |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| Pectolinarigenin from Plants ≥96%
Odor: characteristic Use: Pectolinarin and pectolinarigenin also increased activity levels of glutathione (GSH), glutathione reductase (GR), gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (GCS) and glutathione S-transferase (GST), as well as superoxide dismutase (SOD). The significant effect was only seen in SOD activity. This suggests that the two components exhibit hepatoprotective activity mainly via SOD antioxidant mechanism.
Pectolinarigenin strongly inhibited cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-mediated prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX)-mediated leukotriene (LT) production at >1 microM, indicating that it is a dual inhibitor of COX-2/5-LOX. However, pectolinarigenin did not affect COX-2 expression or nuclear transcription factor (NF-kappaB) activation. In addition, in vivo studies demonstrated that oral administration of these two compounds at 20-100 mg/kg resulted in similar inhibitory activities against several animal models of inflammation/allergy: arachidonic acid-induced mouse ear edema, carrageenan-induced mouse paw edema and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis. All of these results suggest that pectolinarigenin and pectolinarin possess anti-inflammatory activity and that they may inhibit eicosanoid formation in inflammatory lesions. These activities certainly contribute to the anti-inflammatory mechanism of C. chanroenicum. |
Safety Information:
| Hazards identification | |
| Classification of the substance or mixture | |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) | |
| None found. | |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements | |
| Pictogram | |
| Hazard statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
| Dermal Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
| Inhalation Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | natural substances and extractives | ||
| Recommendation for pectolinarigenin usage levels up to: | |||
| not for fragrance use. | |||
| Recommendation for pectolinarigenin flavor usage levels up to: | |||
| not for flavor use. | |||
Safety References:
| EPI System: | View |
| AIDS Citations: | Search |
| Cancer Citations: | Search |
| Toxicology Citations: | Search |
| EPA ACToR: | Toxicology Data |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (SRS): | Registry |
| Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary : | 5320438 |
| National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: | Data |
| 5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | |
| Chemidplus: | 0000520127 |
References:
| 5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | |
| NIST Chemistry WebBook: | Search Inchi |
| Pubchem (cid): | 5320438 |
| Pubchem (sid): | 135025511 |
Other Information:
| (IUPAC): | Atomic Weights of the Elements 2011 (pdf) |
| Videos: | The Periodic Table of Videos |
| tgsc: | Atomic Weights use for this web site |
| (IUPAC): | Periodic Table of the Elements |
| CHEBI: | View |
| CHEMBL: | View |
| KEGG (GenomeNet): | C17784 |
| HMDB (The Human Metabolome Database): | Search |
| FooDB: | FDB005736 |
| VCF-Online: | VCF Volatile Compounds in Food |
| ChemSpider: | View |
| Wikipedia: | View |
Potential Blenders and core components note
| None Found | ||
Potential Uses:
| None Found |
Occurrence (nature, food, other): note
| cirsium japonicum Search Trop Picture | |
| sunflower plant Search Trop Picture | |
| tarragon plant Search Trop Picture |
Synonyms:
| 4H-1- | benzopyran-4-one, 5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)- |
| 5,7- | dihydroxy-4',6-dimethoxyflavone |
| 4,5- | dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-chromen-7-one |
| 5,7- | dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-benzopyrone |
| 5,7- | dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
| 5,7- | dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one |
| 5,7- | dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromen-4-one |
| 5,7- | dihydroxy-6,4'-dimethoxyflavone |
| flavone, 5,7-dihydroxy-4',6-dimethoxy- | |
| flavone, 5,7-dihydroxy-4',6-dimethoxy- (8CI) | |
| 6- | methoxyacacetin |
| pectolinarin | |
| pectolinaringenin |
