|
Category: natural substances and extractives
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
Physical Properties:
| Assay: | 95.00 to 100.00 %
|
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Boiling Point: | 287.00 to 289.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg
|
| Vapor Pressure: | 0.000263 mmHg @ 25.00 °C. (est) |
| Flash Point: | 288.00 °F. TCC ( 142.22 °C. )
|
| logP (o/w): | 1.274 (est) |
| Soluble in: |
| | alcohol | | | water, 2.901e+004 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) |
| Insoluble in: |
| | water |
Organoleptic Properties:
| |
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). |
| |
| |
Cosmetic Information:
Suppliers:
| BOC Sciences |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| 3-Hydroxy octanoic acid ≥98%
Odor: characteristic Use: 3-Hydroxy octanoic acid is a hydroxylated fatty acid that has been found in LPS from P. aeruginosa and the methyl-branched poly |
Safety Information:
| |
| Hazards identification |
| |
| Classification of the substance or mixture |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) |
| None found. |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements |
| |
| Pictogram | |
| |
| Hazard statement(s) |
| None found. |
| Precautionary statement(s) |
| None found. |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
| Dermal Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
| Inhalation Toxicity: |
|
Not determined
|
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | natural substances and extractives |
| Recommendation for 3-hydroxyoctanoic acid usage levels up to: | | | not for fragrance use.
|
| |
| Recommendation for 3-hydroxyoctanoic acid flavor usage levels up to: |
| | not for flavor use.
|
Safety References:
References:
Other Information:
Potential Blenders and core components notePotential Uses:
Occurrence (nature, food, other): noteSynonyms:
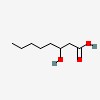
| 3- | hydroxy caprylic acid | | 3- | hydroxycaprylic acid | | (±)-3- | hydroxyoctanoic acid | | 3- | hydroxyoctanoicacid | | | octanoic acid, 3-hydroxy- |
Articles:
| PubMed: | International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXVIII. G protein-coupled receptor list: recommendations for new pairings with cognate ligands. |
| PubMed: | Novel description of mcl-PHA biosynthesis by Pseudomonas chlororaphis from animal-derived waste. |
| PubMed: | Isolation, structure elucidation, and iron-binding properties of lystabactins, siderophores isolated from a marine Pseudoalteromonas sp. |
| PubMed: | Oriental orchid (Cymbidium floribundum) attracts the Japanese honeybee (Apis cerana japonica) with a mixture of 3-hydroxyoctanoic acid and 10-hydroxy- (E)-2-decenoic acid. |
| PubMed: | Hirtionosides A-C, gallates of megastigmane glucosides, 3-hydroxyoctanoic acid glucosides and a phenylpropanoid glucoside from the whole plants of Euphorbia hirta. |
| PubMed: | Functional characterization of an NADPH dependent 2-alkyl-3-ketoalkanoic acid reductase involved in olefin biosynthesis in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. |
| PubMed: | Scytonemides A and B, cyclic peptides with 20S proteasome inhibitory activity from the cultured cyanobacterium Scytonema hofmanii. |
| PubMed: | Genetic replacement of tesB with PTE1 affects chain-length proportions of 3-hydroxyalkanoic acids produced through β-oxidation of oleic acid in Escherichia coli. |
| PubMed: | Production of chiral (R)-3-hydroxyoctanoic acid monomers, catalyzed by Pseudomonas fluorescens GK13 poly(3-hydroxyoctanoic acid) depolymerase. |
| PubMed: | Overexpression and characterization of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate granule bound polymerases from Pseudomonas putida GPo1. |
| PubMed: | Deorphanization of GPR109B as a receptor for the beta-oxidation intermediate 3-OH-octanoic acid and its role in the regulation of lipolysis. |
| PubMed: | Simultaneous accumulation and degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates: futile cycle or clever regulation? |
| PubMed: | Large-scale production of poly(3-hydroxyoctanoic acid) by Pseudomonas putida GPo1 and a simplified downstream process. |
| PubMed: | Reclassification of subspecies of Acidovorax avenae as A. Avenae (Manns 1905) emend., A. cattleyae (Pavarino, 1911) comb. nov., A. citrulli Schaad et al., 1978) comb. nov., and proposal of A. oryzae sp. nov. |
| PubMed: | Microbial production of medium-chain-length 3-hydroxyalkanoic acids by recombinant Pseudomonas putida KT2442 harboring genes fadL, fadD and phaZ. |
| PubMed: | Production of medium-chain-length hydroxyalkanoic acids from Pseudomonas putida in pH stat. |
| PubMed: | Efficient production of (R)-3-hydroxycarboxylic acids by biotechnological conversion of polyhydroxyalkanoates and their purification. |
| PubMed: | Biosynthesis and characterization of deuterated polyhydroxyoctanoate. |
| PubMed: | Biosynthesis of medium-chain-length poly(hydroxyalkanoates) from soy molasses. |
| PubMed: | Biosynthesis of medium chain length poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) (mcl-PHAs) by Comamonas testosteroni during cultivation on vegetable oils. |
| PubMed: | Bacterial poly(hydroxyalkanoates) as a source of chiral hydroxyalkanoic acids. |
| PubMed: | The application of polyhydroxyalkanoates as tissue engineering materials. |
| PubMed: | The wewakpeptins, cyclic depsipeptides from a Papua New Guinea collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena. |
| PubMed: | Microbial production and applications of chiral hydroxyalkanoates. |
| PubMed: | Novel biodegradable copolyesters containing blocks of poly(3-hydroxyoctanoate) and poly(epsilon-caprolactone): synthesis and characterization. |
| PubMed: | Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) biosynthesis in Thermus thermophilus: purification and biochemical properties of PHA synthase. |
| PubMed: | First-order kinetics analysis of monomer composition dependent polyhydroxyalkanoic acid degradation in Pseudomonas spp. |
| PubMed: | Production of D-(--)-3-hydroxyalkanoic acid by recombinant Escherichia coli. |
| PubMed: | Production of chiral R-3-hydroxyalkanoic acids and R-3-hydroxyalkanoic acid methylesters via hydrolytic degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesized by pseudomonads. |
| PubMed: | Development of a process for the biotechnological large-scale production of 4-hydroxyvalerate-containing polyesters and characterization of their physical and mechanical properties. |
| PubMed: | Intracellular degradation of two structurally different polyhydroxyalkanoic acids accumulated in Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas citronellolis from mixtures of octanoic acid and 5-phenylvaleric acid. |
| PubMed: | Accumulation of Poly[(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates] in Pseudomonas oleovorans during growth with octanoate in continuous culture at different dilution rates. |
| PubMed: | Production of polyhydroxyalkanoic acids by Ralstonia eutropha and Pseudomonas oleovorans from an oil remaining from biotechnological rhamnose production. |
| PubMed: | Synthesis of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates in arabidopsis thaliana using intermediates of peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation. |
| PubMed: | 3-, 6- and 7-hydroxyoctanoic acids are metabolites of medium-chain triglycerides and excreted in urine as glucuronides. |
| PubMed: | Substrate specificities of poly(hydroxyalkanoate)-degrading bacteria and active site studies on the extracellular poly(3-hydroxyoctanoic acid) depolymerase of Pseudomonas fluorescens GK13. |
| PubMed: | Molecular characterization of the extracellular poly(3-hydroxyoctanoic acid) [P(3HO)] depolymerase gene of Pseudomonas fluorescens GK13 and of its gene product. |
| PubMed: | Degradation of poly(3-hydroxyoctanoic acid) [P(3HO)] by bacteria: purification and properties of a P(3HO) depolymerase from Pseudomonas fluorescens GK13. |
| PubMed: | Ornibactins--a new family of siderophores from Pseudomonas. |
| PubMed: | Diagnosis of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in lymphocytes and liver by a gas chromatographic method: the effect of oral riboflavin supplementation. |
| PubMed: | 3-Hydroxydicarboxylic aciduria due to long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency associated with sudden neonatal death: protective effect of medium-chain triglyceride treatment. |
| PubMed: | 3-Hydroxyoctanoic aciduria: identification of a new organic acid in the urine of a patient with non-ketotic hypoglycemia. |
| PubMed: | Inhibition of aspartic proteinases by peptides containing lysine and ornithine side-chain analogues of statine. |
| PubMed: | [Volatile acids in tropical fruits: cherimoya (Annona cherimolia, Mill.), guava (psidium guajava, L.), mango (Mangifera indica, L., var. Alphonso), papaya (Carica papaya, L.)]. |
|
 3D/inchi
3D/inchi
