Articles:
N-b-alanyl-L-histidine
Notes:
a naturally occurring dipeptide neuropeptide found in muscles. Occurs in meats
Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) is a dipeptide of the amino acids beta-alanine and histidine. It is highly concentrated in muscle and brain tissues.; Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) is found exclusively in animal tissues. It is a dipeptide of the amino acids beta-alanine and histidine. Carnosine has the potential to suppress many of the biochemical changes (e.g., protein oxidation, glycation, AGE formation, and cross-linking) that accompany aging and associated pathologies (PMID 16804013). It is highly concentrated in muscle and brain tissues. Some autistics patients take it as a dietary supplement, and attribute an improvement in their condition to it. Supplemental carnosine may increase corticosterone levels. This may explain the "hyperactivity" seen in autistic subjects at higher doses. Carnosine also exhibits some antioxidant effects. The antioxidant mechanism of carnosine is attributed to its chelating effect against metal ions, superoxide dismutase (SOD)-like activity, ROS and free radicals scavenging ability (PMID 16406688); Some studies have detected beneficial effects of N-acetyl-carnosine in preventing and treating cataracts of the eyes; in one of these, carnosine was found to reduce cloudiness in rat lenses that were exposed to guanidine to cause cataracts. However, claims that carnosine confers these and other posited ophthamological benefits are, as of yet, insufficiently supported for endorsement by the mainstream medical community; Britain's Royal College of Ophthamologists, for instance, has asserted that neither safety nor efficacy has been sufficiently demonstrated to recommend carnosine's use as a topical treatment for cataracts.
| CAS Number: | 305-84-0 | 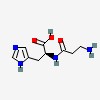 3D/inchi 3D/inchi
|
| Other(deleted CASRN): | 7683-28-5 | |
| ECHA EINECS - REACH Pre-Reg: | 206-169-9 | |
| FDA UNII: | 8HO6PVN24W | |
| Nikkaji Web: | J5.496H | |
| Beilstein Number: | 0087671 | |
| MDL: | MFCD00005207 | |
| XlogP3-AA: | -4.00 (est) | |
| Molecular Weight: | 226.23618000 | |
| Formula: | C9 H14 N4 O3 | |
| BioActivity Summary: | listing | |
| NMR Predictor: | Predict (works with chrome or firefox) | |
Category: cosmetic agents, multi-functional anti-aging peptide
US / EU / FDA / JECFA / FEMA / FLAVIS / Scholar / Patent Information:
| Google Scholar: | Search |
| Google Books: | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "volatile" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "flavor" | Search |
| Google Scholar: with word "odor" | Search |
| Google Patents: | Search |
| US Patents: | Search |
| EU Patents: | Search |
| Pubchem Patents: | Search |
| PubMed: | Search |
| NCBI: | Search |
Physical Properties:
| Appearance: | white powder (est) |
| Assay: | 95.00 to 100.00 % |
| Food Chemicals Codex Listed: | No |
| Melting Point: | 260.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg |
| Boiling Point: | 656.00 to 657.00 °C. @ 760.00 mm Hg (est) |
| Flash Point: | 663.00 °F. TCC ( 350.70 °C. ) (est) |
| logP (o/w): | -2.972 (est) |
| Soluble in: | |
| water | |
| water, 5.503e+004 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) | |
Organoleptic Properties:
| Odor Description: at 100.00 %. | odorless |
| Odor and/or flavor descriptions from others (if found). | |
Cosmetic Information:
| CosIng: | cosmetic data |
| Cosmetic Uses: |
skin conditioning |
Suppliers:
| AIDP |
| L-Carnosine 99% - 101% |
| AuNutra® Industries |
| L-Carnosine |
| BOC Sciences |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| L-Carnosine 95% |
| Charkit Chemical |
| CARNOSINE,L- |
| Glentham Life Sciences |
| L-Carnosine |
| Indis NV |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| L-Carnosine |
| Jiangyin Healthway |
| L-Carnosine |
| New functional food ingredients |
| Kingyoung Bio Technical |
| Carnosine |
| M.C.Biotec |
| Carnosine |
| Meafo |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| L-Carnosine 99% |
| Penta International |
| L-CARNOSINE |
| Sigma-Aldrich: Sigma |
| For experimental / research use only. |
| L-Carnosine ∼99%, crystalline |
| Symrise |
| Dragosine®
Life Essentials - Actives Odor: characteristic Use: Dragosine® (L-Carnosine) is a nature identical dipeptide (β-Alanyl-L-histidin) present in millimolar concentrations in muscle tissues. It protects cells against oxidative stress. In cosmetic products it is used as an anti-aging ingredient which has powerful anti-oxidant properties that stimulate collagen synthesis.
New data confirm that Dragosine® dose dependently and significantly inhibits IRA-induced MMP-1 expression (in vitro assay) and is able to reduce the number of sunburn cells after UV exposure (ex vivo results). |
| Vigon International |
| Dragosine |
Safety Information:
| Preferred SDS: View | |
| Hazards identification | |
| Classification of the substance or mixture | |
| GHS Classification in accordance with 29 CFR 1910 (OSHA HCS) | |
| None found. | |
| GHS Label elements, including precautionary statements | |
| Pictogram | |
| Hazard statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| None found. | |
| Oral/Parenteral Toxicity: | |
|
oral-mouse LD50 > 14930 mg/kg BEHAVIORAL: MUSCLE CONTRACTION OR SPASTICITY) BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION United States Patent Document. Vol. #4446149 intraperitoneal-mouse LD50 9087 mg/kg BEHAVIORAL: MUSCLE CONTRACTION OR SPASTICITY) BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION United States Patent Document. Vol. #4446149 | |
| Dermal Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
| Inhalation Toxicity: | |
| Not determined | |
Safety in Use Information:
| Category: | cosmetic agents, multi-functional anti-aging peptide | ||
| Recommendation for laevo-carnosine usage levels up to: | |||
| not for fragrance use. | |||
| Recommendation for laevo-carnosine flavor usage levels up to: | |||
| not for flavor use. | |||
Safety References:
| European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) reference(s): | |
| Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to beta-alanine and increase in physical performance during short-duration, high-intensity exercise pursuant to Article 13(5) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 View page or View pdf | |
| EPI System: | View |
| ClinicalTrials.gov: | search |
| AIDS Citations: | Search |
| Cancer Citations: | Search |
| Toxicology Citations: | Search |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (TSCA): | 305-84-0 |
| EPA ACToR: | Toxicology Data |
| EPA Substance Registry Services (SRS): | Registry |
| Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary : | 439224 |
| National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: | Data |
| WGK Germany: | 2 |
| (2S)-2-(3-aminopropanoylamino)-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Chemidplus: | 0000305840 |
| RTECS: | MS3080000 for cas# 305-84-0 |
References:
| (2S)-2-(3-aminopropanoylamino)-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid | |
| NIST Chemistry WebBook: | Search Inchi |
| Pubchem (cid): | 439224 |
| Pubchem (sid): | 134974114 |
Other Information:
| (IUPAC): | Atomic Weights of the Elements 2011 (pdf) |
| Videos: | The Periodic Table of Videos |
| tgsc: | Atomic Weights use for this web site |
| (IUPAC): | Periodic Table of the Elements |
| CHEBI: | View |
| CHEMBL: | View |
| Metabolomics Database: | Search |
| KEGG (GenomeNet): | C00386 |
| HMDB (The Human Metabolome Database): | HMDB00033 |
| FooDB: | FDB000511 |
| YMDB (Yeast Metabolome Database): | YMDB01555 |
| Export Tariff Code: | 2933.29.5000 |
| VCF-Online: | VCF Volatile Compounds in Food |
| ChemSpider: | View |
| Wikipedia: | View |
Potential Blenders and core components note
| None Found | ||
Potential Uses:
| None Found |
Occurrence (nature, food, other): note
| found in nature |
Synonyms:
| beta- | alanyl-L-histidine |
| N-b- | alanyl-L-histidine |
| N-(b- | alanyl)-L-histidine |
| (2S)-2-(3- | aminopropanamido)-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid |
| (2S)-2-(3- | aminopropanoylamino)-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid |
| (2S)-2-(3- | aminopropanoylamino)-3-imidazol-4-ylpropanoic acid |
| L- | carnosine |
| dragosine (Symrise) | |
| ignotine |






